Why does DNA polymerase synthesis in a 5 to 3 direction. The lagging strand begins replication by binding with multiple primers.

Veeam Backup And Replication 9 5 Update 3a Released Supporting Vsphere 6 7 Download Now
1Why does DNA replicate from 5.
Why replication always from 5 to 3. I think in order to understand just think of the structure of a nucleotide. Wouldnt that be more efficient. Explain what 5 to 3 means with respect to nucleotide subunits.
Energy formation of the phosphiodiester bond between 5 to. Explain what activity of DNA polymerase necessitates that. See full answer below.
Hence DNA polymerase moves along the template strand in 3 - 5 direction and the daughter strand is formed in a 5 - 3 direction. Replication always starts from 5 because there is OH group present on the strand which allows the addition of free nucleotides. DNA replication goes in the 5 to 3 direction because DNA polymerase acts on the 3-OH of the existing strand for adding free nucleotides.
Explain what activity of DNA polymerase necessitates that replication is 5 to 3. Explain what 5 to 3 means with respect to nucleotide subunits. DNA Replication Before a cell divides via mitosis it needs to generate a.
2 A strand in 5 to 3 direction indicates a free 5. Active 3 years 4 months ago. DNTP is a nucleotide which has two additional phosphates attached to its 5 end.
5 - 3 direction refers to the orientation of nucleotides of a. It sounds like you are very new to molecular biology. View Revisiondocx from AA 11.
DNA replication proceeds only in 5-- 3 direction b. Because the chromosomes are always aligned in the 5 to 3 direction in the nucleus. DNA polymerases require 3 OH group for the initiation of synthesis of DNA strand.
Asked 9 years 8 months ago. Bidirectional Elongation of new strands a. What is the 5 to 3 direction.
DNA replication is always 5 to 3. DNA-polymerase can only work from the 5-end to the 3-end. Why DNA replication or mRNA synthesis are always from 5 to 3 direction.
Which is highly unlikely because if the triphosphate on the. Use our paper writing service to score better and meet your deadlines. View 5_prime_to_3_primepptx from BIOL 351 at Texas AM University.
The enzyme DNA polymerase synthesises strands in the 5 prime to 3 prime direction and as DNA is antiparallel the replication of the leading strand occurs from the 3 prime end of the template to. Why does DNA replication occur from 5 to 3. 31 December 1969 11 4K Report.
1 A nucleotide has a free 5 phosphate end and a free 3 OH end. Each strand of DNA has a 5 end and a 3 end. Each primer is only several bases apart.
DNA is always read in the 5 to 3 direction and hence you would start reading from the free phosphate and finish at the free hydroxyl group. This makes the whole process of DNA replication a very accurate process and this need for accuracy probably explains why the synthesis of new DNA strand always takes place from 5-3 because the exonucleolytic proofreading activity of the DNA polymerase is from 3-5. DNA replication goes in the 5 to 3 direction because DNA polymerase acts on the 3-OH of the existing strand for adding free nucleotides.
Lagging strand - replication fork opening 3 to 5 moving away from replication fork - DNA Pase does NOT work 3-5 4. RNA growth is always in the 5 3 direction. In other words nucleotides are always added at a 3 growing tip as shown in Figure 10-6b.
Because replication proceeds in the 5 to 3 direction on the leading strand the newly formed strand is continuous. Need your ASSIGNMENT done. The replication can occur in 3-5 durection where polymerase would likely need to use the energy provided by the triphosphate from the nucleotide on the DNA strand that is extended and not on the newly added nucleotide.
You will need to do a LOT of basic background reading to understand your project. In eukaryotic cells polymerases alpha delta and epsilon are the primary polymerases involved in DNA replication. Why does DNA replication go from 5 to 3.
Shivansh Gaur MSc Biotechnology - CSJMU Kanpur. In order to make that strand longer you could imagine adding new DNA. Therefore it can synthesize in only one direction by extending the 3 end of the pre-existing nucleotide chain.
End instead of from 3 to 5 end. DNA polymerase will add the free DNA nucleotides using complementary base pairing A-T and C-G to the 3 end of the primer this will allow the new DNA strand to form. It uses the OH on the 3 end of a nucleotide to attach a phosphate from the 5.
Because DNA Polymerase requires the OH on the 3 as an active site. Why are nucleotides added to 3 end. Order a Similar Paper Order a Different Paper DNA replication is always 5 to 3.
Because of the antiparallel nature of the nucleotide pairing the fact that RNA is synthesized 5 3 means that the template strand must be oriented 3 5. Leading strand - polymerase adds nucleotides continuously 5--3 from origin site - follows replication fork c. 2Why do we need DNA polymerase I and not just DNA polymerase III if polymerase I is just initiating DNA replication and polymerase III does all the heavy lifting and continues it why dont we just use polymerase III.
Aamal Ghazi Mahdi Al-Saadi Aamal_Ghazi_Al-Saadi. DNA replication only occurs in the 5 to 3 direction because DNA polymerase requires a free 3 hydroxyl group to attach the new nucleotide to. The process of DNA replication always starts from the 5 to 3 direction because the nucleotides are added to the 3 end of a polynucleotide strand or.
DNA replication goes in the 5 to 3 direction because DNA polymerase acts on the 3-OH of the existing strand for adding free nucleotides. When a textbook states that DNA can only be replicated in the 5 to 3 direction it is referring to the synthesis of DNA. Why replication only happens from 5 to 3 From the proofreading aspect Replication from 5 to 3 P P P 5 P P P.

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable

Figure 5 9 Exonucleolytic Proofreading By Dna Polymerase During Dna Replication Molecular Biology Of The Ce Teaching Biology Biochemistry Molecular Genetics

Dna Replication Leading Strand Vs Lagging Strand Okazaki Fragments Youtube

The Genetic Code Shmoop Biology Biology Biology Classroom Genetics

In Dna Replication Small Rna Primer Dna Replication Molecular Biology Molecular

Medicowesome Dna Replication Mnemonics Mnemonics Medical Humor Behavioral Science

Replication Fork Teaching Biology Study Biology Biology College
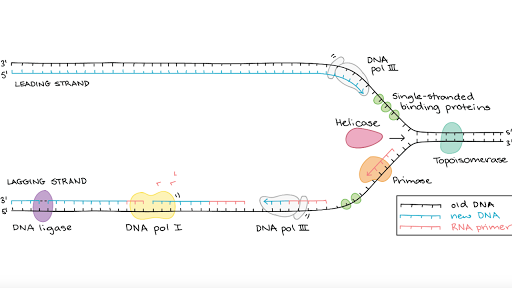
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Why Can T Dna Polymerase Attach Things To The 5 End Of A Strand Of Dna
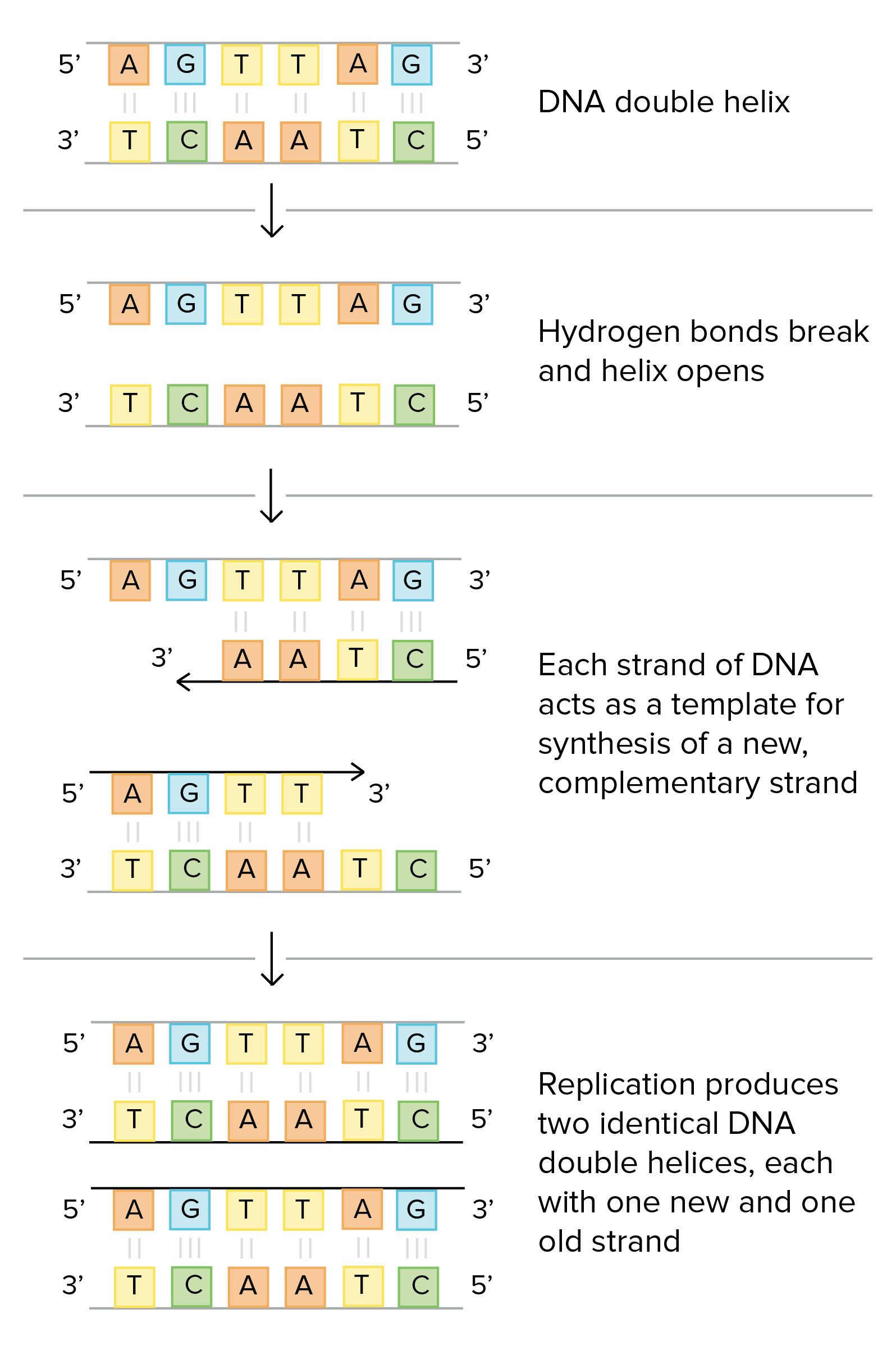
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Why Can T Dna Polymerase Attach Things To The 5 End Of A Strand Of Dna

Why Can T Dna Polymerase Attach Things To The 5 End Of A Strand Of Dna

Dna Replication Concept Map Biology Lessons Study Biology Teaching Biology

Steps And Proteins Involved In Dna Replication Dna Polymerase Mitochondrial Dna Dna Ligase

Structure And Diagrams Of Dna Replication Dna Replication Structure And Diagrams Dna Replication Structure And Diagrams Human Body Science Dna Biology Notes

Amoebasisters Confused About What Is Meant By 5 To 3 And 3 To 5 In Dna We Have A Gif For That Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Science Biology
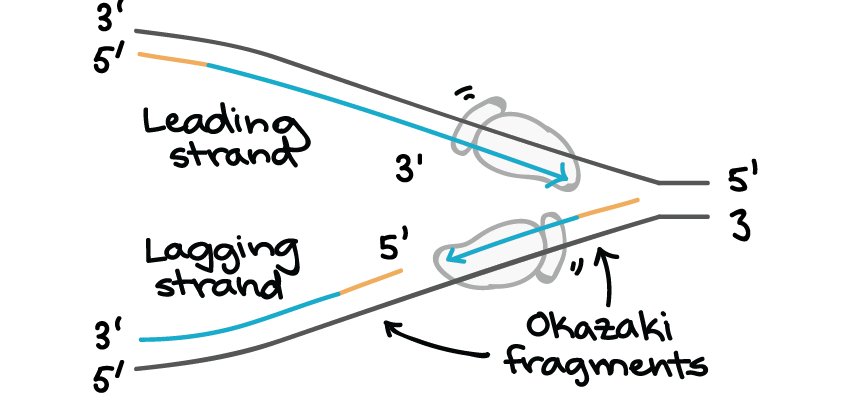
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

13 Dna Replication And Rna Transcription And Translation Video Khan Aca Dna Transcription Transcription And Translation Dna Transcription And Translation

